To gain a deeper understanding of the value of digital skills and how they can transform lives, Gallup and AWS partnered to conduct the largest international survey of its type, polling nearly 30,000 workers and 9,300 hiring managers in 19 countries. In addition, to assess the skills most needed by today’s employers, Gallup analyzed Lightcast (formerly Emsi Burning Glass) data on all advertised job vacancies in 33 countries from mid-2021 to mid-2022. Complete findings are available in The 2022 AWS Global Digital Skills Study: The Economic Benefits of a Tech-Savvy Workforce.
As information technology continues to transform our lives and work, new research from Gallup and Amazon Web Services (AWS) sheds light on the tremendous economic, innovation, and performance benefits that investing in advanced digital skills for workers can provide.
The research—a part of Amazon’s ongoing commitment to provide free cloud computing skills training to 29 million people by 2025—offers five key insights.
Digital skills yield big economic benefits
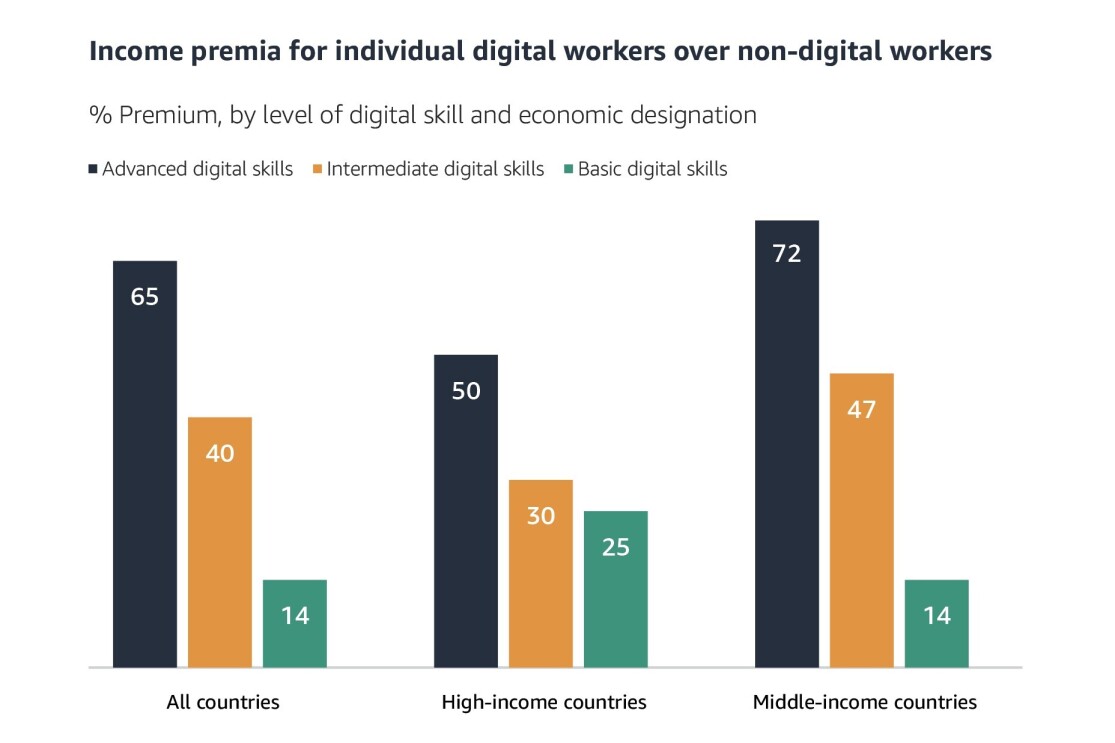
Digital skills generate income and revenue premiums for workers and industries. This quickly adds up to major global value. The data shows that advanced digital skills alone—such as cloud architecture and software development—raise annual global gross domestic product (GDP) by an estimated $6.3 trillion by boosting the income and productivity of workers. Additionally, companies with high levels of digital skill utilization report annual revenues that are approximately 168% higher than companies that do not use digital skills. Workers see the benefits too. Across the 19 countries sampled, workers with intermediate skills—including understanding of cloud concepts and ability to use tools like drag-and-drop websites—earned 40% more than individuals with basic digital skills, like email and word processing. For individuals with advanced skills, including using programming languages, the difference in earnings jumped to 65%.
Digital skills generate income and revenue premiums for workers and industries. This quickly adds up to major global value. The data shows that advanced digital skills alone—such as cloud architecture and software development—raise annual global gross domestic product (GDP) by an estimated $6.3 trillion by boosting the income and productivity of workers. Additionally, companies with high levels of digital skill utilization report annual revenues that are approximately 168% higher than companies that do not use digital skills. Workers see the benefits too. Across the 19 countries sampled, workers with intermediate skills—including understanding of cloud concepts and ability to use tools like drag-and-drop websites—earned 40% more than individuals with basic digital skills, like email and word processing. For individuals with advanced skills, including using programming languages, the difference in earnings jumped to 65%.
Workers’ benefits increase as digital skills knowledge increases
Employees know the value of digital skills, and nearly all (98%) agree that training in a digital skill has benefitted their career. More than three-quarters (77%) of digital workers are “extremely interested” or “very interested” in learning new digital skills. This is good news for employees who continue to express a challenge in finding qualified talent. More than two-thirds of companies (70%) report hiring challenges when it comes to roles requiring digital skills.
Employees know the value of digital skills, and nearly all (98%) agree that training in a digital skill has benefitted their career. More than three-quarters (77%) of digital workers are “extremely interested” or “very interested” in learning new digital skills. This is good news for employees who continue to express a challenge in finding qualified talent. More than two-thirds of companies (70%) report hiring challenges when it comes to roles requiring digital skills.
Additionally, the survey reveals a meaningful link between digital skill mastery and gains in employee job satisfaction. Nearly three out of four (72%) of workers with advanced digital skills evaluate their job as close to ideal, compared to less than half of workers with basic digital skills (43%). Similarly, workers with advanced digital skills expressed higher levels of job security (72% versus 48%).
Investing in digital skills delivers big dividends for businesses
Research also reveals that organizations that integrate advanced digital skills, digital technologies, and cloud technologies consistently outperform nondigital peers. Companies that employ advanced digital workers—such as cloud engineers and software developers—are about 50% more likely to report innovating in the past two years than companies that only use basic digital technologies like email and messaging apps. Additionally, 66% of companies that run some or most of their business in the cloud reported innovating products or services in the past two years, a rate five times higher than companies that do not use the cloud and do not plan to adopt it in the future.
Research also reveals that organizations that integrate advanced digital skills, digital technologies, and cloud technologies consistently outperform nondigital peers. Companies that employ advanced digital workers—such as cloud engineers and software developers—are about 50% more likely to report innovating in the past two years than companies that only use basic digital technologies like email and messaging apps. Additionally, 66% of companies that run some or most of their business in the cloud reported innovating products or services in the past two years, a rate five times higher than companies that do not use the cloud and do not plan to adopt it in the future.
5G, cryptocurrency and the Metaverse are here to stay
While most organizations already say hiring for the digital skills they need is a challenge, they also need to prepare for the hiring challenges of the future. The innovation of new, disruptive technologies shows no sign of stopping. When asked how likely it is that 10 such emerging technologies will become a standard part of their business in the future, 65% of global employers rated the likelihood of at least one technology as an eight or higher on a scale of zero to 10. More than half (52%) believe multiple technologies will become standard, and 11% say all 10 will be part of their organization’s business in the future.
While most organizations already say hiring for the digital skills they need is a challenge, they also need to prepare for the hiring challenges of the future. The innovation of new, disruptive technologies shows no sign of stopping. When asked how likely it is that 10 such emerging technologies will become a standard part of their business in the future, 65% of global employers rated the likelihood of at least one technology as an eight or higher on a scale of zero to 10. More than half (52%) believe multiple technologies will become standard, and 11% say all 10 will be part of their organization’s business in the future.
Global report highlights:
Trending news and stories