November 30, 2023 7:21 PM
That's a wrap on AWS re:Invent 2023
November 30, 2023 7:19 PM
See what it’s like inside an Amazon Web Services data center
Generative artificial intelligence (generative AI) has been the talk of the town at AWS re:Invent this week, from AWS-designed custom chips to generative AI assistants to the latest foundation models. But have you ever wondered what it’s like inside a data center, where all those machine learning workloads are running? Take a look at the final episode in our ‘Data Centered’ series, a day in the life of three AWS data center employees in eastern Oregon.
November 30, 2023 7:16 PM
Cloud meets sustainability with interactive installations
AWS re:Invent attendees can visit the Sustainability Showcase to see demos of wildfire remote detection and monitoring; simulated ecological changes in Madagascar; the use of generative artificial intelligence (generative AI) to help ingest and analyze environmental, social, and governance (ESG)-related information to enhance sustainability decision-making; and renewable energy assets monitoring.
The installations are designed to educate and inspire organizations across all sectors on how they can leverage AWS services, including generative AI and machine learning, to drive sustainability progress.
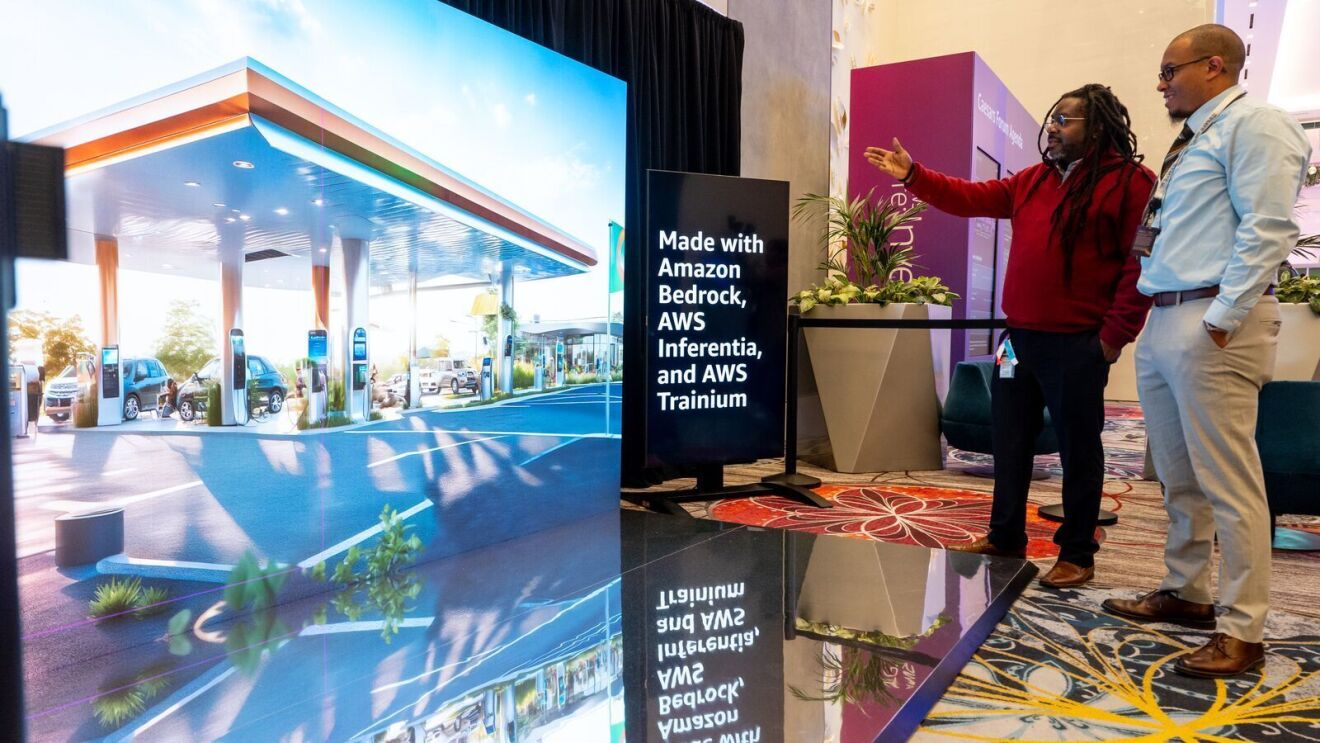

Powered by Amazon Bedrock, one demo is equal parts artistry and inspiration. A large LED screen takes viewers through a series of scenarios powered by generative AI that asks the question, “What if we made different decisions with the same resources?” The AI model then produces an ever-changing series of answers in the form of changing landscapes, buildings, streets, and more.
November 30, 2023 6:30 PM
Generative AI startup founders make their first trip to re:Invent
Sisters Jhanvi and Ketaki Shriram have created a first-of-its-kind text-to-3D animation tool that allows users to build customizable avatars doing everything from Bollywood dancing to football plays—with no technical skill.
Krikey AI runs on a proprietary foundation model that works with Amazon’s Sagemaker to create animations based on a user’s text commands or video uploads, with no coding required.
01 / 03
The siblings had a busy week at AWS re:Invent, giving demos of their generative AI-powered 3D animation company, Krikey AI, to a global audience. From the field of the Allegiant Stadium, where they shared their app with fellow startup leaders and venture capitalists, to their Q & A on the floor of the expo hall, the founders showed off the fruits of their 7-year journey from game developers to generative AI animation experts.
CTO Ketaki shared the stage Thursday with AWS product leaders to discuss how her team used human-in-the-loop technology with Amazon SageMaker Ground Truth to expedite their process of labeling hundreds of thousands of datapoints.
“We’re currently building the largest 3D human motion dataset in the world. We’ve already trained it so quickly, and we couldn’t have done it without Ground Truth and AWS.”
November 30, 2023 6:07 PM
As climate change fuels wildfire risks, these companies use AWS to fight back
As global temperatures continue to rise, so does the expected size, frequency, and intensity of wildfires. At re:Invent, four Amazon Web Services (AWS) customers shared how they’re using the latest AWS technologies to combat wildfires.

Analyzing satellite images for early wildfire detection
The same technology that scientists use to find new galaxies light-years away can also be used to detect wildfires here on Earth. Satellite cameras pointed at Earth offer images rich with data, including indicators of wildfires. Australian-based company exci uses artificial intelligence (AI) models trained on more than a billion images to accurately detect wildfires and alert local officials.
Estimating wildfire risk, property by property
A lot of people might read sprawling government reports or look at complicated charts and not understand how wildfire risk applies to them, at an individual level. First Street Foundation, a nonprofit dedicated to making climate risk information more accessible, estimates the wildfire risk of every building and property in the contiguous U.S. People can visit riskfactor.com, enter their address, and see their risk factor on a scale of 1–10.
Scouring social media for wildfire clues
Kablamo is a technology solutions partner, crafting built-for-the-cloud digital products and data platforms, including wildfire detection tools. Working with the Rural Fire Service in New South Wales, Australia, the company built Athena, a system that assesses wildfire risk, helps plan for fuel reduction activities, and uses AI to comb through social media posts, looking for content about wildfires.
Using machine learning and drones for wildfire prevention
As fires get larger and occur more frequently, spotting and fixing potential electrical equipment failures becomes truly vital for electric utilities. San Diego Gas & Electric (SDGE) is combining the long experience of their qualified electrical workers, a bird’s-eye view of the utility’s equipment captured by a fleet of drones, and powerful machine learning (ML) models running on AWS. The drones take images to help identify equipment potentially in need of repair. SDGE also uses AI to help better predict which circuits are most prone to fires due to adverse weather conditions.
November 30, 2023 4:49 PM
It’s an exciting time to be a developer
Developers need to become “Frugal Architects,” said Amazon.com Vice President and Chief Technology Officer Werner Vogels, at re:Invent Thursday, sharing a set of simple rules for building cost-aware, sustainable, and modern architectures.
There’s so much technology out there competing for businesses’ attention, he pointed out, but they can’t afford to chase all of it. Instead, Vogels recommended that builders think of cost as what he called a “nonfunctional requirement of development.” In other words, consider cost early and continuously when you’re designing, developing, and operating your systems in order to balance features, time-to-market, and efficiency.
Conversely, it’s also important to constantly align development decisions with the needs of the business, which typically means delivering systems and applications that will save customers money. The architecture, Vogels said, must follow the money. To illustrate his point, Vogels mentioned how Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) saved 80% in streaming costs by re-architecting for the cloud.
Cat Swetel, senior director of engineering at Brazil’s Nubank, joined Vogels on stage to describe how costs were a key element in her institution’s successful delivery of a 24/7, no-fee, instant money transfer program called “Pix.” As Pix’s popularity quickly grew, Nubank systems had to handle exponentially larger and more intense workloads. They were left with a choice: buy more equipment and capacity or re-architect to solve the problem more frugally. They chose the latter approach and, as a result, saw improved stability, more predictable workloads, and a 92% decrease in latency. More importantly, she noted, the bank’s 9 million customers saved $8 billion in fees in 2022.
Vogels said developers also need to think about the connection between business costs and costs to the planet. Environmental sustainability as a fundamental element of software development is a “freight train coming your way,” he said, “and you can’t escape it.”
Fortunately, Vogels noted that cost is a close proxy for sustainability. If businesses are architecting for costs and tracking financial impact along the way, they should be able to estimate their environmental impact, as well. As an example, he pointed to WeTransfer, a Dutch computer file transfer service, which he said experienced a 78% emissions reduction after re-architecting, tracking, and measuring server systems.
Sustainability is just one of the things developers should keep top of mind with respect to doing right by people and the planet, Vogels said. For example, he noted that Cergenx, an Ireland-based neonatal neurotechnology company, is using artificial intelligence (AI) to quickly identify newborn infants at risk of birth-related brain injury. He also pointed to Digital Earth Africa, an organization collecting and analyzing satellite imagery to help governments around the world track environmental concerns like deforestation and erosion.
Dr. Rebecca Portnoff, head of data science for Thorn, took the stage to explain how her nonprofit organization is providing machine learning (ML)-based tools that scour millions of digital files worldwide looking for possible instances of sexual abuse against children. With more than 88 million files reviewed in 2022, Portnoff said it could literally take three years for a human being to find a single abuse “needle” in that “haystack” of files. But with ML acting as a magnet to pull out those needles, she said, the process is light years faster.
Vogels said that such innovation is part of what’s making software so exciting these days. He said there is a clear opportunity for technologies like AI and ML to do the heavy lifting, making coding faster and easier, but human beings will always be integrally involved in guiding it along and making decisions.
November 30, 2023 3:31 PM
Here’s how FlexZero uses generative AI for carbon tracking and reporting

Dr. David Johnsen, previously a sustainability application architect at Amazon Web Services (AWS), has seen companies around the globe face the same sustainability challenges—how to model their business activities with enough detail to accurately track, report, and reduce carbon emissions.
“Companies want to reduce their carbon emissions and need data to achieve this,” Johnsen said. “We saw that customer need over and over again.”
With fellow solutions architect Ravi Raghunathan, he set out to make a tool that guides customers through three steps. First, what are my carbon emissions today? Second, how do I report on them? Third, how do I start reducing my output?
The result is the sustainability platform they founded, FlexZero, a carbon management and disclosure tool built entirely on AWS and demoed at the re:Invent expo this week. It enables customers to track their carbon data, generate actionable insights, and reduce their emissions. For example, a shipping company might connect data about the distance a truck travels and how much weight it carries. Then, FlexZero processes that information to estimate carbon emissions, either using calculations with industry standard emission factors, such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency or the UK Department for Environment Food and Rural Affairs, or customer specific emission factors.
The platform uses AWS products and services, including AWS Lambda to run serverless code and Amazon Textract to extract printed text and data from documents. And by harnessing Amazon Bedrock, FlexZero integrates custom generative artificial intelligence (generative AI) into its carbon emissions analysis and reporting.
A customer could use the FlexZero chat feature to ask, “Which scope category should I target for reduction within my top five factories?” Or, “What do we need to do for our LA office to be compliant with California SB253,” and the platform will provide specific guidance.
The app is flexible (as reflected in its name), and customers can define the data it ingests, how they want the app to process the data, and which reports it should produce.
“Maybe you have an office, maybe you travel, maybe you make something,” Johnsen said. “FlexZero is industry agnostic.”
November 30, 2023 12:26 PM
New AWS Rec Center serves up AI-powered sports challenges for re:Invent attendees
Attendees at this year’s re:Invent can go to the event’s new Rec Center and experience firsthand how Amazon Web Services (AWS) innovates in the sports industry.
The Rec Center features games inspired by some of the major sports leagues that work with AWS, including Bundesliga and NFL. There are also other sports-related challenges, such as generative artificial intelligence (generative AI)-powered robotic chess.
Bundesliga Free Kick Challenge
The Bundesliga Free Kick Challenge debuted at re:Invent in 2022 and is back with new underlying technology. The AWS prototyping team has implemented ball tracking with computer vision (CV) running on AWS Panorama, trained with Amazon SageMaker. Two cameras, flexing a 200Hz frame rate and connected to an AWS Panorama Appliance, track the speed and accuracy of soccer balls as attendees kick them into a goal roughly 13 yards (12 meters) away.
The Bundesliga Free Kick Challenge debuted at re:Invent in 2022 and is back with new underlying technology. The AWS prototyping team has implemented ball tracking with computer vision (CV) running on AWS Panorama, trained with Amazon SageMaker. Two cameras, flexing a 200Hz frame rate and connected to an AWS Panorama Appliance, track the speed and accuracy of soccer balls as attendees kick them into a goal roughly 13 yards (12 meters) away.
NFL Passing Challenge
In advance of the Super Bowl coming to Las Vegas this season, attendees can throw a football at the NFL Passing Challenge to see how they measure up to NFL quarterbacks. The ball’s speed and trajectory are tracked in real time using Zebra Technologies’ ultra-precise location technology. Tracking data is then streamed to the cloud with Amazon Kinesis Data Streams, where it is stored in Amazon Redshift and analyzed in real time using Amazon SageMaker. Together, these technologies power Next Gen Stats, the real-time insights used during live NFL broadcasts.
In advance of the Super Bowl coming to Las Vegas this season, attendees can throw a football at the NFL Passing Challenge to see how they measure up to NFL quarterbacks. The ball’s speed and trajectory are tracked in real time using Zebra Technologies’ ultra-precise location technology. Tracking data is then streamed to the cloud with Amazon Kinesis Data Streams, where it is stored in Amazon Redshift and analyzed in real time using Amazon SageMaker. Together, these technologies power Next Gen Stats, the real-time insights used during live NFL broadcasts.
Generative AI-powered robotic chess
On the Rec Center’s chessboard, two advanced robotic arms engage in an epic game, powered by cutting-edge AI and state-of-the-art robotic control. These highly articulated arms are equipped with advanced sensors, ensuring accurate manipulation of chess pieces. And they use AWS generative AI models for advanced learning and reinforcement techniques, constantly evolving their gameplay strategies based on extensive training data. This project showcases the incredible potential of intelligent automation and the seamless integration of robotics with AWS generative AI capabilities.
On the Rec Center’s chessboard, two advanced robotic arms engage in an epic game, powered by cutting-edge AI and state-of-the-art robotic control. These highly articulated arms are equipped with advanced sensors, ensuring accurate manipulation of chess pieces. And they use AWS generative AI models for advanced learning and reinforcement techniques, constantly evolving their gameplay strategies based on extensive training data. This project showcases the incredible potential of intelligent automation and the seamless integration of robotics with AWS generative AI capabilities.
November 30, 2023 10:06 AM
AWS Partners make the impossible possible
With technology advancing at such a rapid pace, strong industry partnerships will be crucial in helping customers take advantage of it. That was the message from Ruba Borno, Amazon Web Services (AWS) vice president of Worldwide Channels and Alliances, in her re:Invent keynote.
Borno said this is particularly true when it comes to generative artificial Intelligence (generative AI), which a recent McKinsey report found could eventually contribute up to $4.4 trillion to the global economy. Customers attempting to move from using the technology in pilot to actual production need help ensuring they get the underlying data foundations right first. And such transformation is often too time-consuming and complex for them to handle on their own.
That’s why AWS works with a vibrant and growing community of more than 150,000 partners to push the boundaries of what’s possible and overcome the impossible for customers, Borno said.
Here are some highlights from her keynote.
- A new collaboration between AWS and professional services company Accenture will help developers and enterprise customers accelerate the adoption of Amazon Q.
- A new strategic collaboration between AWS and digital workflow company ServiceNow will help customers put AI to work in their businesses. Customers will see the ServiceNow Platform become available as a software as a service (SaaS) offering in the AWS Marketplace in 2024.
- Blackstone, a global investment company managing $1 trillion in assets, is working with AWS and Pinecone, a vector database provider, to deliver a generative AI–based solution to empower their investor teams.
- Hotelier Marriott International is working with AWS, consultancy firm Deloitte, and software vendor Palo Alto Networks to deliver digital guest services more safely and securely with AI, according to Arno Van Der Walt, chief information security officer for Marriott.
- Documentary streaming service MagellanTV worked with AWS Partner Mission Cloud to create a generative AI solution on AWS to automate the workflow of translating, transcribing, and dubbing its content into various languages. According to MagellanTV co-founder Thomas Lucas, the automated solution “redefined the economics of distribution” by dramatically cutting the cost of these activities.
- The U.S. Air Force worked with AWS and partner C3 AI to roll out a machine learning (ML) project that’s helped reduce costs, improve efficiency, and predict the performance of its fleet of about 5,000 aircraft. C3 AI has been working with the Air Force since 2008 to make sense of its data, and more recently started applying ML to identify aircraft component issues so planes can be scheduled for maintenance or repair before these issues become larger problems that result in downtime.
Joining Borno onstage toward the end, AWS CEO Adam Selipsky underscored the importance of partners in helping AWS support customers around the world.
November 30, 2023 7:00 AM
Amazon CTO Dr. Werner Vogels shares 4 tech predictions for 2024
Amazon CTO Dr. Werner Vogels offers his insights on the technological advances on the horizon, from culturally aware artificial intelligence (AI) to FemTech to the evolution of tech education.
November 29, 2023 6:48 PM
Why human ingenuity will continue to be the driving force of innovation
The relationship between people and automated technology can trace its roots to the 1880s, Swami Sivasubramanian, AWS vice president of Data and AI, told the re:Invent audience during his keynote Wednesday.
Back then, mathematician Ada Lovelace suggested future generations of computers would be able to handle complex tasks, and even produce art and music. But she maintained they would still need direction for creative ideas from their human counterparts, as machines can’t really originate anything on their own.
Sivasubramanian said such thinking was an early ode to the potential of generative artificial intelligence (generative AI). As effective as it may be, it’s still in its early stages and remains entirely dependent on clean data and human input for its success. Data, generative AI, and people can complement each other to deliver innovation and better experiences for customers.
To illustrate the point, he gave a hypothetical example of using our generative AI service Amazon Bedrock to create apps for do-it-yourselfers (DIYers) to pursue projects more simply and efficiently. DIYers would be able to use natural language to ask such an app about any type of project and receive a list of detailed steps, materials, tools, and recommendations for completing it. The app would use customer inputs to generate images of their project to inspire the user’s work and direction. And it would also be able to search its data resources to offer product suggestions, reviews, and pricing.
 A photo of Nhung Ho, vice president of AI, Intuit
A photo of Nhung Ho, vice president of AI, IntuitSivasubramanian was joined by Nhung Ho, VP of AI at global financial technology platform Intuit. She told the audience how Amazon Sagemaker is a foundational capability for the company, allowing its entire community of machine learning developers to build, deploy, and ship new AI experiences with speed.
Next, Aravind Srinivas CEO and co-founder of Perplexity AI, described how his company is working with AWS to reimagine the future of web search through its generative AI chatbot, Copilot. He said the tool uses commercial, open source, and its own online large language models (LLMs), released this month, to unlock knowledge with information discovery and sharing. AWS tools and technologies play a big part in bringing all those models together, Srinivas said.
 Aravind Srinivas CEO and co-founder of Perplexity AI
Aravind Srinivas CEO and co-founder of Perplexity AIFollowing Perplexity, Brian Kursar, group vice president, digital technology, and Ashley Parks, senior devops engineer at Toyota Motor Corp. explained how the automaker embeds hundreds of sensors in its vehicles to gather safety-related data, such as whether the vehicle has been in a collision requiring an emergency response. Processing petabytes of such data worldwide in real time when every second counts presented an enormous engineering challenge that the breadth of the AWS portfolio was able to address. If an issue occurs, the technology triggers an alert in the AWS Cloud, and then an employee from the call center then reaches out to drivers within seconds. Toyota is also experimenting with generative AI, the executives said. In fact, using Amazon Bedrock, the automaker was able to ingest the owner’s manual and develop a generative AI–powered assistant that will be able to give drivers information about their car in response to simple voice commands.
Beyond business, Sivasubramanian emphasized generative AI can also improve the health and welfare of people around the world, regardless of their location. In fact, he delivered this point when co-presenting with Dr. Kingsley Ndoh, founder of Hurone AI, at a U.N. General Assembly event in New York in September.
In all these cases, people, data, and technology come together to deliver an array of possibilities. As Lovelace suggested more than a century ago, people will continue to be the driving force of innovation, helped by a powerful new technology to inspire their thinking and creativity.
November 29, 2023 6:09 PM
How generative AI is improving cancer care for patients around the world
Artificial intelligence (AI) is bringing cancer patients new types of care—with more efficiency and better outcomes. That’s according to the expert panel of pathologists, doctors and medical technologists who met at re:Invent. They discussed how future innovation in cancer diagnosis and drug discovery will rely on the scalability and security of the cloud, along with new advancements in generative artificial intelligence (generative AI).

“Technology’s not a silver bullet to end cancer,” said moderator Dr. Rowland Illing, chief medical officer and director of international public sector health at AWS. ”But it is an enabler to support the real heroes—the researchers, the healthcare providers, the caregivers, and of course, the patients.“
For home care technology provider AlayaCare, based in Canada, generative AI tools help to automate repetitive tasks that can be time-consuming for professionals who provide in-home chemotherapy treatments. Amazon Bedrock automatically extracts important data from patient forms and care plans, and turns that information into actionable summaries so nurses and doctors have the insights they need quickly.
For Hurone AI, a startup creating a system for remote cancer care in several African countries, Bedrock is used in similar ways, allowing doctors to communicate more efficiently with faraway patients through an AI-powered cellphone application. Hurone AI CEO and Founder Kingsley Ndoh said time is a physician’s greatest asset. “If we can save them time, that will transform patient care.”
For pathologists, generative AI is being used to create better practices in cancer diagnostics. Historically that has been a very analog process, with a pathologist looking down a microscope, reading a glass slide to determinate the diagnosis.
Genomics England, for example, is building a multimodal research platform, digitizing hundreds of thousands of pathology and radiology images. They use AWS to make roughly 100 petabytes of data searchable in a secure environment in the cloud. The panel also talked about legal and ethical guardrails, agreeing the human expertise plays a key role in how future cancer care innovation will advance.
“There's no algorithm that replaces experience,” Ndoh said. “Generative AI is basically a tool to support doctors, but there's a human in the loop. We are at the beginning of that journey and things will continue to evolve.”
November 29, 2023 5:37 PM
Try your hand as a race car driver or a quarterback with generative AI
Do you want to be at the helm of an F1-inspired slot car? Or see a football field through the eyes of an NFL quarterback?
The re:Invent Expo hall is the place to do that roleplaying—and then some. For example, the NFL Next Gen Stats Defense Decoder interactive exhibit lets you step into the shoes of an NFL quarterback and feel the pressure of making the perfect play. It uses three AI-powered screens to recreate a quarterback’s point-of-view and tasks players to correctly identify which side the defense will be blitzing from. If race cars are more your speed, an F1-sponsored slot car demo shows how AWS AI and ML are used for racing analytics, car telemetry and defect detection.
The expo is host to nearly 400 AWS Partner booths where attendees can learn about software, data, and services—all running on AWS. There are four distinct zones: 1) Data, 2) Developer Solutions, 3) Infrastructure Solutions, and 4) Security, and at the center of each zone is a cluster of AWS exhibits that provide a better understanding of the application of our services.
Anyone curious about learning opportunities can dive in at All Builders Welcome Lounge; the AWS Village; the AWS Community Developer Lounge; the AWS Training and Certification Lounge; or the Builders’ Fair. The AWS for Industries Pavilion is also part of the Expo, where industry partners share interactive demos and show how they are helping customers to innovate.
November 29, 2023 4:14 PM
New innovations help customers use AI responsibly
A new survey commissioned by AWS and conducted by Morning Consult of a representative sample of business leaders in the U.S. unveils the growing importance of responsible AI as more companies and organizations are putting generative AI to work for their business.
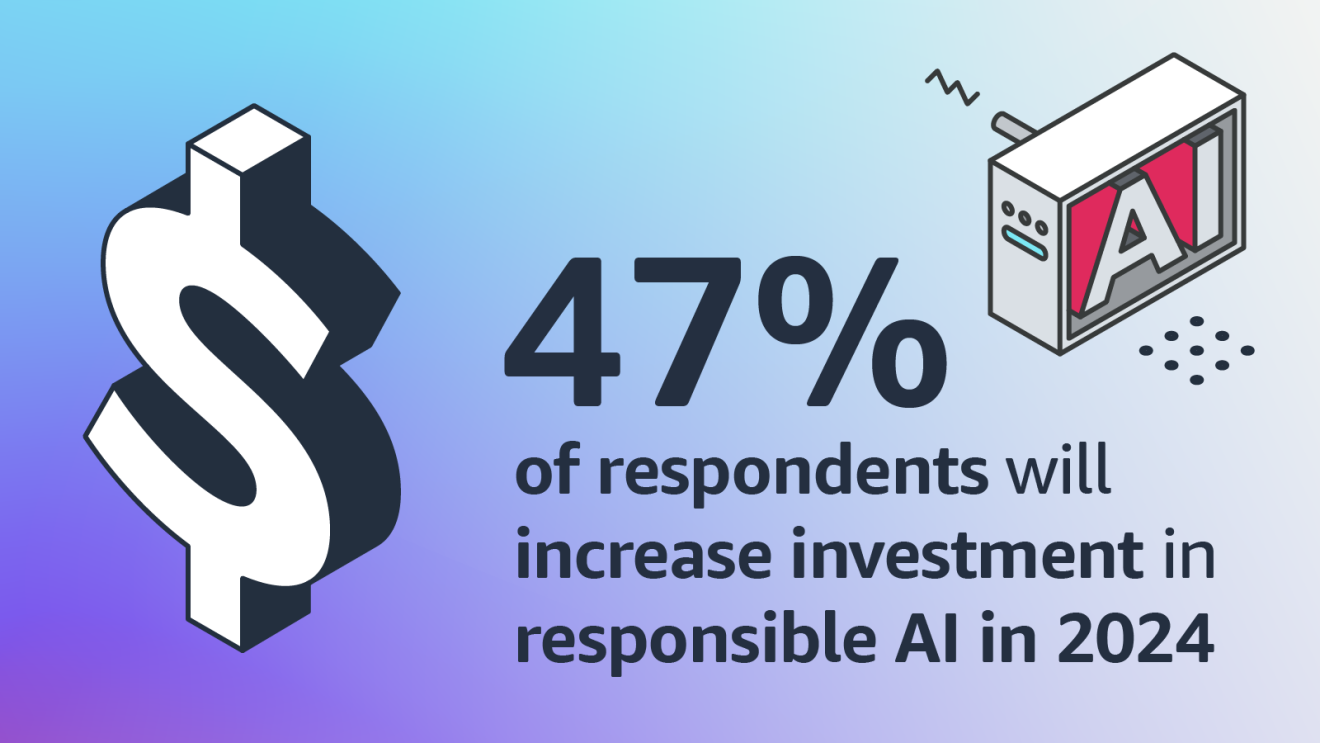
77% of respondents say they are familiar with responsible AI, and nearly half (47%) of respondents plan to invest more in responsible AI in 2024 than in 2023. The research also shows that younger business leaders appear to be ahead of their more seasoned peers in terms of familiarity with responsible AI and an intention to implement a strategy around it. Read a more in-depth summary of the findings.
As responsible AI becomes increasingly top-of-mind for business leaders, AWS announced this week new innovations at re:Invent to help its customers design, build, and deploy AI responsibly. To name a few, Guardrails for Amazon Bedrock helps customers implement safeguards customized to their generative AI applications and aligned with their responsible AI policies.
Model Evaluation on Amazon Bedrock, now available in preview, helps customers evaluate, compare, and select the best FMs based on metrics important to their use case, such as accuracy and toxicity, using either automatic or human evaluations. And, building on the commitments AWS made earlier this year at the White House, Amazon Titan applies an invisible watermark to all images it generates to help reduce the spread of disinformation by providing a discreet mechanism to identify AI-generated images and to promote the safe, secure, and transparent development of AI technology. AWS is among the first model providers to widely release built-in invisible watermarks that are integrated into the image outputs and are designed to be resistant to alterations. Last but not least, AWS now offers copyright indemnity coverage for outputs of all generally available Titan models and other applications with generative output. Learn more about these innovations that help customers invest in responsible AI across the entire AI lifecycle.
November 29, 2023 3:11 PM
Booking.com uses AWS generative AI to match travelers with trips beyond their expectations
Booking.com, one of the world’s leading travel platforms, is using generative artificial intelligence (generative AI) technology to enhance the search and booking process for customers.
Rob Francis, senior vice president and chief technology officer of Booking.com, joined Swami Sivasubramanian, vice president of Data and AI at Amazon Web Services (AWS), on the mainstage of re:Invent to highlight how the travel company uses AWS technology.
 Rob Francis, senior vice president and chief technology officer of Booking.com
Rob Francis, senior vice president and chief technology officer of Booking.comFrancis said Booking.com’s journey with AWS started in 2021, when it was looking for a partner to overcome challenges in latency and data limitations, as well as take advantage of emerging technology.
Booking.com wanted to use generative AI to match people with experiences that went beyond their expectations. It built AI Trip Planner, a chat-based tool that allows users to ask travel-related questions, like those scoping out accommodation options or creating detailed itineraries. Travelers can also describe what they’re looking for—a quiet beach in the Caribbean or a list of vacation homes with a pool for a family of four—and AI Trip Planner will make recommendations in a quick, conversational way.
The tool uses Amazon SageMaker to power a process called Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), which gathers data outside of foundation models. For example, it combs through years’ of guest reviews to pull insights about accommodations and experiences, and uses that data to shape its travel advice.
Looking to the future, the Booking.com team continues to optimize the AI Trip Planner as it rolls out beyond the U.S., and the team is now experimenting with Amazon Bedrock and Amazon Titan to explore how they might enhance experiences for both customers and supply partners.
November 29, 2023 12:00 PM
What is Generative AI and How Does it Work?
Generative artificial intelligence (generative AI ) is a big theme for re:Invent this year. You can use generative AI to create new content of all kinds, whether something simple, like writing custom captions for images or far more complex, like developing more effective drug molecules. But how? Here’s a breakdown of what it is and how it works.
November 29, 2023 11:15 AM
5 new Amazon SageMaker capabilities make it easier to build, train, and deploy models for generative AI
 AWS Vice President of Data and AI Swami Sivasubramanian
AWS Vice President of Data and AI Swami SivasubramanianOne of the things that makes generative artificial intelligence (generative AI) so exciting for businesses and organizations of all kinds is its ability to be used out of the box for a wide variety of tasks.
The technology can do this thanks to its use of large language models (LLMs) and other foundation models (FMs)—highly adaptable machine learning models that are pre-trained on vast amounts of data. This morning at re:Invent, AWS Vice President of Data and AI Swami Sivasubramanian announced five new capabilities for Amazon SageMaker, our fully managed service that brings together a broad set of tools to enable high-performance, low-cost machine learning for any use case.
Here are the new capabilities that will make it even easier for customers to build, train, and deploy models for generative AI.
SageMaker HyperPod
Accelerates model training time by up to 40% by enabling customers to automatically split training workloads across hundreds or thousands of accelerators, so workloads can be processed in parallel for improved model performance.
Accelerates model training time by up to 40% by enabling customers to automatically split training workloads across hundreds or thousands of accelerators, so workloads can be processed in parallel for improved model performance.
SageMaker Inference
Allows customers to deploy multiple models to the same AWS instance (virtual server), to better use the underlying accelerators and reduce deployment costs and latency.
Allows customers to deploy multiple models to the same AWS instance (virtual server), to better use the underlying accelerators and reduce deployment costs and latency.
SageMaker Clarify
Helps customers evaluate, compare, and select the best models for their specific use case, based on their chosen parameter to support responsible use of AI.
Helps customers evaluate, compare, and select the best models for their specific use case, based on their chosen parameter to support responsible use of AI.
SageMaker Canvas enhancements
Two new launches in Canvas make it easier and faster for customers to integrate generative AI into their workflows.
Two new launches in Canvas make it easier and faster for customers to integrate generative AI into their workflows.
November 29, 2023 10:26 AM
Expanded choice of industry-leading models in Amazon Bedrock for generative AI applications
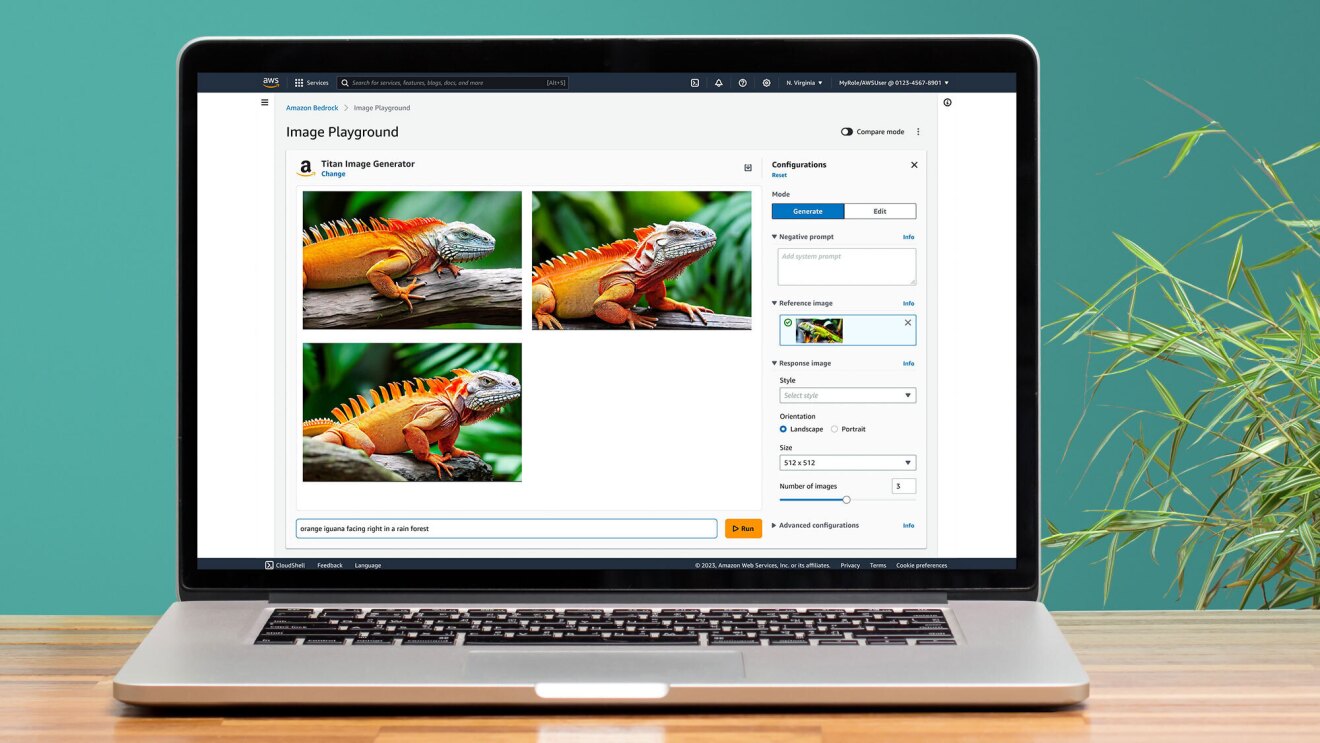 This iguana image is getting a few updated looks with the help of Amazon Titan Image Generator.
This iguana image is getting a few updated looks with the help of Amazon Titan Image Generator.Foundation models (FMs) are very large, highly customizable machine learning models that are pre-trained on vast amounts of data, including text and images. With Amazon Bedrock, customers can drive rapid innovation with the latest versions of these models. In his re:Invent keynote this morning, AWS Vice President of Data and AI Swami Sivasubramanian announced that we’re offering customers even more choice of models to build and scale generative artificial intelligence (generative AI) applications. This includes additions from Anthropic, Cohere, Meta, and Stability AI, as well as new models in the Amazon Titan family and a new model capability in Amazon Bedrock to help evaluate them.
Why? Because no single model is ideal for every use case. Models vary across capabilities, price, and performance, and customers need easy access to a variety of model choices, so they can try different models, switch among them, and combine the best models for their needs. Here are some of the new models.
Anthropic’s Claude 2.1 in Amazon Bedrock
Anthropic, an AI safety and research company, has brought Claude 2.1, the latest version of its language model, to Amazon Bedrock. Claude 2.1 offers a 200,000 token context window and improved accuracy over long documents. Models understand the meaning of a “token” (in this case, words) by looking at the other tokens around it. The “context window” is the range of tokens, or words, the model can consider when responding to a prompt. A larger context window means more tokens, better performance, and greater accuracy. Customers can now process text-heavy documents such as financial statements and internal datasets, and Claude 2.1 can summarize, perform Q&A, and much more. Now generally available in Amazon Bedrock.
Anthropic, an AI safety and research company, has brought Claude 2.1, the latest version of its language model, to Amazon Bedrock. Claude 2.1 offers a 200,000 token context window and improved accuracy over long documents. Models understand the meaning of a “token” (in this case, words) by looking at the other tokens around it. The “context window” is the range of tokens, or words, the model can consider when responding to a prompt. A larger context window means more tokens, better performance, and greater accuracy. Customers can now process text-heavy documents such as financial statements and internal datasets, and Claude 2.1 can summarize, perform Q&A, and much more. Now generally available in Amazon Bedrock.
Meta Llama 2 70B in Amazon Bedrock
Llama 2 is the next generation of language models by Meta. Llama 2 was trained on 40% more data than Llama 1 and has double the context length. Llama 2 is optimized for dialog use cases through fine-tuning with instruction datasets and more than 1 million human annotations. Now generally available in Amazon Bedrock.
Llama 2 is the next generation of language models by Meta. Llama 2 was trained on 40% more data than Llama 1 and has double the context length. Llama 2 is optimized for dialog use cases through fine-tuning with instruction datasets and more than 1 million human annotations. Now generally available in Amazon Bedrock.
New Amazon Titan Multimodal Embeddings
Amazon Titan Multimodal Embeddings helps customers power more accurate and contextually relevant search and recommendation experiences for end users. “Multimodal” refers to the fact that the model can generate embeddings—numerical representations that allow it to easily understand semantic meanings and relationships among data—for both image and text, which are stored in a customer’s vector database. End users can submit search queries using any combination of image and text prompts. For example, a stock photography company with hundreds of millions of images can use the model to power its search functionality, so users can search for images using a phrase such as “show me images similar to the provided image but with sunny skies.” Now generally available.
Amazon Titan Multimodal Embeddings helps customers power more accurate and contextually relevant search and recommendation experiences for end users. “Multimodal” refers to the fact that the model can generate embeddings—numerical representations that allow it to easily understand semantic meanings and relationships among data—for both image and text, which are stored in a customer’s vector database. End users can submit search queries using any combination of image and text prompts. For example, a stock photography company with hundreds of millions of images can use the model to power its search functionality, so users can search for images using a phrase such as “show me images similar to the provided image but with sunny skies.” Now generally available.
 AWS Vice President of Data and AI Swami Sivasubramanian
AWS Vice President of Data and AI Swami SivasubramanianNew Amazon Titan Image Generator
Designed to help customers in industries such as advertising, ecommerce, and media and entertainment produce or enhance studio-quality, realistic images, using natural language prompts, for rapid ideation and iteration on large volumes of images and at low cost. The model can understand complex prompts and generate relevant images with accurate object composition and limited distortions, reducing the generation of harmful content and mitigating the spread of misinformation. Building on the commitments AWS made earlier this year at the White House, Amazon Titan applies an invisible watermark to all images it generates to help reduce the spread of misinformation by providing a discrete mechanism to identify AI-generated images and to promote the safe, secure, and transparent development of AI technology. Available in preview.
Designed to help customers in industries such as advertising, ecommerce, and media and entertainment produce or enhance studio-quality, realistic images, using natural language prompts, for rapid ideation and iteration on large volumes of images and at low cost. The model can understand complex prompts and generate relevant images with accurate object composition and limited distortions, reducing the generation of harmful content and mitigating the spread of misinformation. Building on the commitments AWS made earlier this year at the White House, Amazon Titan applies an invisible watermark to all images it generates to help reduce the spread of misinformation by providing a discrete mechanism to identify AI-generated images and to promote the safe, secure, and transparent development of AI technology. Available in preview.
November 28, 2023 9:27 PM
AWS CEO outlines rapid progress with generative AI tools, services, and more during re:Invent
In his re:Invent keynote Tuesday morning, Amazon Web Services (AWS) CEO Adam Selipsky outlined how we’re delivering a host of innovations to help companies move from simply testing generative artificial intelligence (generative AI) to using it to deliver real business gains.
Topping the list: A powerful new generative AI assistant called Amazon Q that’s specifically for work and can be tailored to your business. Employees can use Amazon Q to hold conversations, solve problems, generate content, gain insights, and act on them by seamlessly tapping into corporate information repositories, code, data, and enterprise systems.
NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang joined Selipsky to describe how the company is collaborating with AWS to build the first cloud AI supercomputer, built on the NVIDIA GH200 NVL32 Grace Hopper Superchip and AWS’s UltraClusters. AWS was the first cloud provider to recognize the importance of graphics processing unit (GPU)-accelerated computing, Huang told attendees.
 AWS CEO Adam Selipsky (Left) and NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang (Right)
AWS CEO Adam Selipsky (Left) and NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang (Right)Later, Dario Amodei, CEO of Anthropic, an AI safety and research company in which Amazon is investing up to $4 billion, explained to the re:Invent audience how the large language models (LLMs) supporting his company’s AI assistant, Claude, have been trained on AWS infrastructure. He said AWS is Anthropic’s primary cloud provider for mission-critical workloads across industries from health care to information and financial services.
Next up: Lydia Fonseca, executive vice president and technology officer for pharmaceutical company Pfizer. Fonseca described how digital, data, and AI are critical for developing new medications for patients faster. Pfizer migrated to AWS in 2021, Fonseca said, and as a result, it’s been able to significantly speed the development, approval, and delivery of new medicines worldwide while reducing supply chain disruptions. Recently, Pfizer has used generative AI to achieve annual cost savings of $750 million to $1 billion, and it’s rolled out an internal generative AI platform using AWS capabilities, Fonseca added.
 Lydia Fonseca, executive vice president and technology officer for pharmaceutical company Pfizer
Lydia Fonseca, executive vice president and technology officer for pharmaceutical company PfizerShifting from pharma to automotive, Stephan Durach, senior vice president of connected company and technical operations for BMW Group, discussed how the German automaker enhanced the technology stack for its in-car entertainment systems using AWS technology. The company created a cloud data hub leveraging AWS services and is using AI to develop optimized route guidance that will consider everything from real-time traffic to driving styles. Durach said BMW is also working to further integrate Amazon Alexa technology into vehicle guidance and entertainment systems.
Lastly, Selipsky turned to the importance of empowering people in organizations to use AWS Cloud technologies in their jobs. But he noted there is a skills gap that will continue to grow as generative AI becomes a more integral part of the mix.
He emphasized AWS’s commitment to training 29 million people for free in cloud computing by 2025. As examples, he pointed to the recent launch of the AWS Cloud Institute as well as 100 other AI and ML courses. On top of that, the company last week announced the new AI Ready effort to provide free AI skills training to an additional 2 million people globally by 2025. AWS has also established a global AI and ML Scholarship program, Selipsky added, while sharing testimonials from several students who greatly benefited from taking part.
November 28, 2023 8:32 PM
Can I bring my pet in the cabin on a Delta flight? Generative AI knows the answer
 Photo by Delta Air Lines Inc.
Photo by Delta Air Lines Inc.Amazon Web Services (AWS) CEO Adam Selipsky highlighted Delta Air Lines Inc.’s customer service tool in his re:Invent keynote today. The new tool is built on Amazon Bedrock and will be able to answer customer questions in a more conversational style by accessing Delta’s travel policies, real-time flight schedules, customer rebooking options, and airport conditions.
For instance, it can respond to questions ranging anywhere from a simple one like, “How many bags can I check on a Delta flight?” to something more complex like, “Can I carry a pet with me in the cabin to Jamaica?”
Delta has been testing with multiple foundation models on Amazon Bedrock, including Anthropic Claude 2.0, Claude Instant, and a fine-tuned Amazon Titan Text Express model, to use the right model to answer different customer questions. The Amazon Titan Text Embeddings model is also being used to retrieve the most relevant information needed to answer a question.
With the new customer service tool, Delta Air Lines is aiming to provide a delightful and conversational self-service experience and improve customer satisfaction.
November 28, 2023 6:02 PM
How to get started with Amazon Q
AWS Vice President of Artificial Intelligence Matt Wood explains how easy it is to configure and customize Amazon Q for your organization.
November 28, 2023 12:21 PM
AWS chips to support a more sustainable future for data centers
 AWS CEO Adam Selipsky
AWS CEO Adam SelipskyAs generative artificial intelligence (generative AI) becomes mainstream, continually innovating to improve power efficiency is critical to sustainably power the workloads of the future. One of the most visible ways we are improving power efficiency is our investment in Amazon Web Services (AWS)-designed chips. Our AWS Graviton processor is based on the Arm architecture, which delivers high performance with high levels of energy efficiency. Graviton4, launched today, will be the most powerful and energy-efficient AWS processor to date. Graviton4 provides up to 30% better compute performance and 75% more memory bandwidth than current generation Graviton3 processors, delivering the best price performance and energy efficiency for a broad range of workloads running on Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2).
In 2022, we launched AWS Trainium, a high-performance machine learning chip designed to reduce the time and cost of training generative AI models—cutting training time for some models from months to weeks, or even days. This, in turn, means building new models requires less money and power, with potential cost savings of up to 50% and energy-consumption reductions of up to 29%, versus comparable instances. Our second-generation Trainium2 chips, unveiled today, are designed to deliver up to four times faster training than first-generation Trainium chips. It will be able to be deployed in EC2 UltraClusters of up to 100,000 chips, making it possible to train large language models (LLMs) and other foundation models (FMs) and do so in a fraction of the time, while improving energy efficiency almost twofold.

These innovations, and others like them, support Amazon’s commitment to reaching net-zero carbon by 2040. As the world’s largest corporate buyer of renewable energy for the last three years, we are on a path to powering our operations with 100% renewable energy by 2025, including AWS data centers.
November 28, 2023 11:33 AM
Project Kuiper announces option for private connectivity to AWS

Project Kuiper is Amazon’s low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite broadband network. In addition to preparing to serve tens of millions of customers in unserved and underserved communities around the world, Project Kuiper will also connect a wide range of enterprise, telecommunications, and public sector customers. AWS CEO Adam Selipsky revealed at re:Invent a new private connectivity option for enterprise and public sector customers of Project Kuiper and AWS. Private connectivity will allow those customers to securely connect any site served by Project Kuiper directly to their AWS resources, without ever touching the internet. That means customers have the flexibility to connect remote people, facilities, and equipment without compromising security, privacy, or compliance standards. Learn more about private connectivity and how Project Kuiper leverages AWS to scale its network.
November 28, 2023 11:22 AM
4 new integrations for AWS services mean customers get their data faster and more easily
Customers will be able to access and analyze data from multiple sources without having to manage custom data pipelines, thanks to four new integrations for existing Amazon Web Services (AWS) offerings. Traditionally, if customers wanted to connect all of their data sources to discover new insights, they’d need—in computing parlance—to “extract, transform, and load” (ETL) information in what was often a tedious and time-consuming manual effort. The new integrations are part of our investment in a “zero ETL future,” where customers can easily get their data where they need it. Find out how we’re making it easier for customers to integrate data from across their entire system, so they can discover new insights, innovate faster, and make better, data-driven decisions.
November 28, 2023 11:08 AM
Getting goods to the right place at the right time in a more sustainable way

Building on the launch of AWS Supply Chain at last year’s re:Invent, this year sees the addition of four new capabilities for the service—supply planning, collaboration, sustainability, and a generative artificial intelligence (generative AI) assistant, Amazon Q. AWS Supply Chain is a cloud-based application that draws on Amazon’s nearly 30 years of supply chain experience to give businesses in any industry a real-time, unified view of their supply chain data. Its new capabilities will include helping customers with forecasting, replenishing products to reduce inventory costs and respond more quickly to demand, and streamlining communication with suppliers. It will also make it easier to request, collect, and audit sustainability data. The new generative AI capability provides a summarized view of key risks around inventory levels and demand variability, and visualizes the tradeoffs between different possible scenarios. Learn more.
November 28, 2023 10:48 AM
How Amazon Q in Connect is transforming customer service with generative AI

Our cloud contact center Amazon Connect already helps organizations of all sizes deliver improved customer experiences at lower cost. Thanks to generative artificial intelligence (generative AI) and Amazon Q—a new type of generative AI assistant that is specifically for work and can be tailored to your business—it’s about to get even better. Amazon Q in Connect helps customer service agents respond even faster to customer requests by assisting agents with proposed responses, suggested actions, and links to relevant articles based on what a customer is saying in the moment. And now, contact center administrators can create even smarter chatbots for customer self-service experiences, simply by describing in plain English what they want the bot to accomplish. Learn more about the Amazon Q in Connect.
November 28, 2023 10:36 AM
Amazon Q is your new expert assistant
From Amazon Alexa to online chatbots, most of us are accustomed to receiving help from artificial intelligence (AI) in our daily lives. But a generative AI-powered assistant that is specifically for work and can be tailored to your business? One that understands the work you do, who you interact with, what information you use, and what you can access, all in the context of your role? That’s been another story—until now.
AWS CEO Adam Selipsky invited AWS Vice President of Artificial Intelligence Matt Wood on stage during his keynote this morning to announce Amazon Q, a new type of generative AI assistant, built with security and privacy in mind, designed to unlock the full potential of this transformational technology for employees at organizations of all sizes and across industries.
If you’re a developer, for example, Amazon Q can assist you in building, deploying, and operating workloads on AWS. If you’re a contact center agent, it can help you formulate customer responses and respond to queries quickly and accurately. For example, Amazon Q could detect a customer is contacting your rental car company to change their reservation. It would then generate a response you could send, detailing the company’s change policies and guide you through the step-by-step process of updating the reservation.

Employees can chat with Amazon Q via a conversational interface, ask questions, receive relevant and reliable answers, generate content, and take actions, all informed by Amazon Q’s understanding of their company’s information repositories, code bases, and enterprise systems. It personalizes its interactions with individual employees, helping them with everything from streamlining tasks to making speedier decisions, accelerating problem solving, generating content, and troubleshooting problems, as well as encouraging creativity and innovation.
November 28, 2023 9:32 AM
AWS CEO Adam Selipsky announces powerful new capabilities for generative AI service Amazon Bedrock

In October, we announced the general availability of Amazon Bedrock, a fully managed AWS service that makes large language models and other foundation models (FMs) from leading artificial intelligence (AI) companies, including AI21, Anthropic, Cohere, Meta, and Stability AI, available through a single API. FMs are very large, highly customized machine learning models that are pre-trained on vast amounts of data, including text and images. AWS CEO Adam Selipsky just announced a range of new capabilities for Amazon Bedrock in his keynote this morning to empower customers to customize models, enable generative AI applications to execute multistep tasks, and build safeguards into their applications. These powerful new capabilities include:
Guardrails for Amazon Bedrock
Helps customers implement safeguards customized to their generative AI applications and aligned with their responsible AI principles. Now available in preview.
Helps customers implement safeguards customized to their generative AI applications and aligned with their responsible AI principles. Now available in preview.
Knowledge Bases for Amazon Bedrock
Makes it even easier to build generative AI applications that use proprietary data to deliver customized, up-to-date responses for use cases such as chatbots and question-answering systems. Now generally available.
Makes it even easier to build generative AI applications that use proprietary data to deliver customized, up-to-date responses for use cases such as chatbots and question-answering systems. Now generally available.
Agents for Amazon Bedrock
Enables generative AI applications to execute multistep business tasks using company systems and data sources. For example, answering questions about product availability or taking sales orders. Now generally available.
Enables generative AI applications to execute multistep business tasks using company systems and data sources. For example, answering questions about product availability or taking sales orders. Now generally available.
Fine-tuning for Amazon Bedrock
Customers have more options to customize models in Amazon Bedrock with fine-tuning support for Cohere Command Lite, Meta Llama 2, and Amazon Titan Text models, with Anthropic Claude coming soon.
Customers have more options to customize models in Amazon Bedrock with fine-tuning support for Cohere Command Lite, Meta Llama 2, and Amazon Titan Text models, with Anthropic Claude coming soon.
Together, these new additions to Amazon Bedrock transform how organizations of all sizes and across all industries can use generative AI to spark innovation and reinvent customer experiences.
November 28, 2023 8:38 AM
Next generation AWS chips will make running generative AI faster, less expensive, and more energy efficient
01 / 02
The foundation models that underpin so much of today’s emerging generative AI activity are trained on massive datasets, something that can involve thousands of computers working in parallel for weeks. Customers want the ability to train these models even faster and at lower cost, and they also want to do this while reducing the amount of energy they use for these, as well as for a broad range of other workloads. That’s why we continue to evolve the designs of our own families of custom chips—AWS Graviton processors and AWS Trainium accelerators—to help customers speed up their workloads, including machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) applications, at lower cost, and for less and less energy. Find out more about AWS Graviton4 and AWS Trainium2, our next generation of AWS-designed chips.
November 28, 2023 8:17 AM
Welcome to the Express Zone—the speediest Amazon S3 storage class ever provides 10 times faster access to data
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is one of the most popular cloud object storage services, holding more than 350 trillion “objects,” or pieces of data, and averaging more than 100 million requests for data a second. Amazon S3 Express One Zone, launched today, is a new, purpose-built Amazon S3 storage class designed to provide data access speeds up to 10 times faster, with request costs up to 50% lower than Amazon S3 standard. Why? Because some customers are running applications that are incredibly latency sensitive, or in other words, require extremely fast data access to achieve the highest possible efficiency. For example, training some machine learning and generative artificial intelligence (generative AI) models often requires millions of images and lines of text to be processed in minutes. Learn more about how Amazon S3 Express One Zone is helping customers accelerate their data processing.
November 28, 2023 8:11 AM
Peter DeSantis kicks off AWS re:Invent with serverless and quantum computing updates
The future of cloud computing lies in serverless computing. But for many companies, the dream of serverless—where they build and run applications without having to manage their own physical servers—is complex and elusive.
That’s why Amazon Web Services (AWS) has been actively innovating to deliver a range of semiconductor, networking, storage, and computing service solutions to “remove the muck of caring for servers,” according to Peter DeSantis, senior vice president of AWS Utility Computing.
Kicking off the 12th annual AWS re:Invent conference in Las Vegas Monday night, DeSantis announced three new serverless innovations that build on the work AWS has been doing ever since we launched with our first service, Amazon S3 (simple storage service) in 2006:
DeSantis was joined on stage by Brent Rich, head of global infrastructure and operations at Riot Games, known for League of Legends, VALORANT, and other popular video games.
Riot Games uses several AWS services to power new experiences for gamers globally. But it wasn’t always that way. Indeed, when League of Legends launched in 2009, Riot Games relied entirely on co-located data centers it controlled because it hadn’t fully migrated to the cloud.
But after attracting more than 100 million League users eight years later, its servers were overloaded— bogging down and impacting the experience of its gamers, said Rich. The company started looking at options, and quickly decided to go all-in with AWS. Riot also decided that all of its new offerings would be born in the cloud, which ultimately led to the development and 2020 release of VALORANT, a game with an estimated 17.2 million active players.
Rich said one of the more interesting advantages of using smooth-running AWS serverless infrastructure to develop and host VALORANT was how it allowed them to minimize the effects of an annoying glitch called a “Peeker’s Advantage,” where a synchronization issue between host servers and user computers gave some gamers an unfair edge over others by letting them to see what competitors were doing before they could respond.
Rich and his team worked closely with the AWS team to find the right solutions for their cloud needs. And while you may not be running a company that requires infrastructure for millions of people to play a game live, Rich had some advice. Regardless of the size of your company, if you have a problem you think AWS can help you solve, don’t hesitate. “Make the ask,” Rich said.
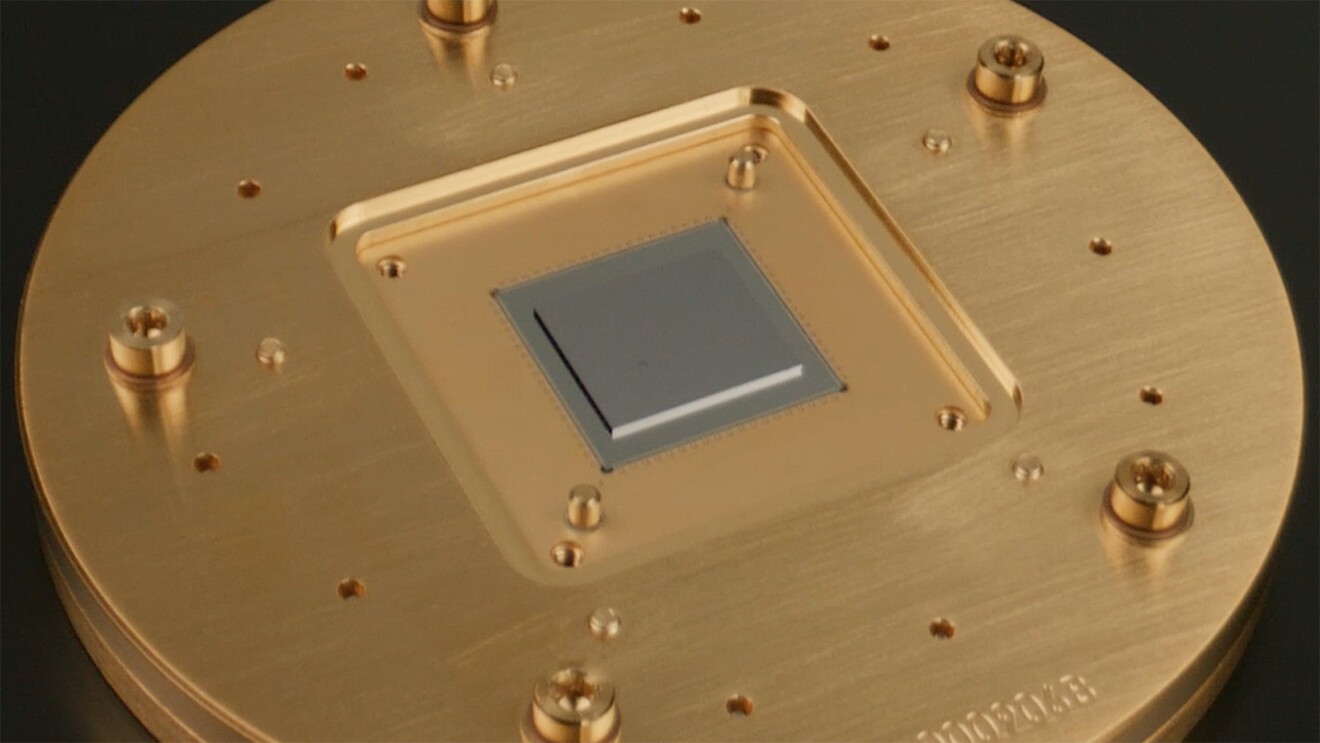 Superconducting-qubit quantum chip
Superconducting-qubit quantum chipDeSantis closed out his keynote with a look into the present and future for Quantum giving the audience a sneak peek of a chip built in-house at the AWS Center for Quantum Computing. The golden disc DeSantis held in his hand housed a square chip engineered to reduce “bit flip” errors. When combined with another “active” error correction technique, it allows AWS engineers to reduce quantum error correction by 6X. Errors cause “noise” and are one of the main hurdles in moving quantum computing from theory to practice. It’s a step we need to take as DeSantis said, “To solve interesting problems on a Quantum computer.”
November 27, 2023 11:00 PM
Wrapping up with Monday Night Live at AWS re:Invent
 A photo of Peter DeSantis, senior vice president of AWS Utility Computing on stage at AWS re:Invent 2023.
A photo of Peter DeSantis, senior vice president of AWS Utility Computing on stage at AWS re:Invent 2023.Peter DeSantis, senior vice president of AWS Utility Computing, kicked off the keynotes at re:Invent by continuing the Monday Night Live tradition, where he shared the latest serverless innovations across our database and analytics portfolio.
Much more is to come this week, starting tomorrow with AWS CEO Adam Selipsky, who will take the main stage, and highlight data, infrastructure, AI, and machine learning innovations that are helping customers achieve their goals faster.
November 27, 2023 9:01 PM
Access your office building by scanning your palm with Amazon One Enterprise
01 / 02
If you have a habit of repeatedly losing your badge or key fob for your office building, Amazon One Enterprise could help make your day a whole lot easier. The new palm recognition identity service enables organizations to give employees and other authorized users fast, convenient, and contactless access to physical locations, such as offices, data centers, hotels, resorts, and educational institutions, simply by scanning the palm of their hand. It can also be used to provide access to restricted software assets, such as financial data or HR records. Learn more about how Amazon One Enterprise works, and how it’s designed to improve security, prevent breaches, and reduce costs, all while protecting people’s personal data.
November 27, 2023 8:32 PM
3 innovations in AWS serverless computing help customers make the most of their data at any scale

Serverless computing is a way for customers to build and run applications without having to manage their own physical servers. Our broad range of serverless data analytics offerings make it easy for customers to take advantage of benefits like automatic provisioning (in other words, automated methods of setting up infrastructure, on-demand scaling, and pay-for-use pricing). So rather than dealing with hardware, developers can focus on building and releasing applications more quickly and at lower cost. Peter DeSantis, senior vice president of AWS Utility Computing, just announced three new AWS serverless innovations that build on the work we’ve been doing since our earliest days to help customers analyze and manage data at any scale, while dramatically simplifying their operations. Learn more about how new serverless innovations for Amazon Aurora, Amazon Redshift, and Amazon ElastiCache will allow customers to do things such as scale capacity to meet their most demanding applications at a moment’s notice.
November 27, 2023 5:43 PM
A mouthy alien robot brings AI down to earth
He appears much slimier than your average robot. And sassier. Wormhole is his name, and he looks other-worldly, perhaps out of a sci-fi movie.

A team from the creative agency Experience.Monks built the creature they call the “AI Alien Robot” using the connective tissue of AWS’s AI tools, including Amazon Bedrock, Amazon Sagemaker, and Amazon Polly. It’s a model of the types of human-to-robot creations they make using artificial intelligence. From animatronic robots to digital avatars, the team is known for creating one-of-a-kind immersive digital projects for global brands.
“We’ve been building experiences with AI for more than six years,” said Iran Reyes, global head of engineering at Experience.Monks. “Now, with gen AI, the possibilities just increase immensely.“
At AWS re:Invent, a group of engineers and executives from Sao Paolo and Toronto showed off Wormhole’s conversational skills. The AI alien robot answered human prompts about everything from Las Vegas activities to generative AI.
Once a question is asked by a human, Whisper (a pre-trained model for automatic speech recognition (ASR) and speech translation) hosted on SageMaker, transcribes the query. Next, a proprietary serverless bot-creation tool built on Amazon Bedrock serves up an answer. Amazon Polly then turns text responses into lifelike alien speech.
As he wrapped a conversation with the AI-alien, Reyes asked Wormhole what he thought of re:Invent so far. The robot’s reply? “AWS rules Vegas, baby!”
November 27, 2023 2:09 PM
Fill it forward with AWS and LaunchDarkly’s reusable water bottle and QR Code
re:Invent attendees are helping provide clean water to an elementary school in Cambodia, while also doing away with tens of thousands of plastic bottles.
Next to the stream of people flooding through the main hall at re:Invent 2023 in Las Vegas is another line of people, each one waiting to carry a pair of yellow water jugs through a short, winding course. The jugs weigh 40 pounds each. After just a quick walk with their liquid load, the lesson is very clear—lugging water for any distance is backbreaking work.
“We want attendees to experience how hard it is for many people around the world who have to do this every day to get clean water,” said Matt Wittek, founder and CEO of Fill it Forward, an organization that creates interactive technologies, global giving initiatives, and reusable products to inspire people to reuse. “Hopefully, they also come away with an understanding of how fortunate we all are to have access to clean water.”
When their walk is complete, each participant receives a reminder to use the purple and orange refillable aluminum water bottle everyone attending re:Invent received when they picked up their badges. That is part two of the lesson, helping folks make more sustainable choices. Emblazoned on the water bottle is a QR Code that takes the whole experience into the realm of direct action.

Each time a re:Invent attendee refills their bottle and scans the code, AWS and cosponsor LaunchDarkly donate $5 to Fill it Forward. The money raised during the course of re:Invent will be used to build a clean water facility at an elementary school in Cambodia, as well as upgrade the school’s sanitation infrastructure.
The fundraising won’t stop after re:Invent. Every time people refill their bottles, they can scan the QR Code and help raise money for other clean water projects.
For more on how you can get involved in bringing clean water to people around the world, head to Fill it Forward.
November 27, 2023 8:00 AM
AWS unveils new low-cost, secure devices built for the modern workplace

For the first time, AWS adapted a consumer device into an external hardware product for AWS customers: the Amazon WorkSpaces Thin Client.
Take a look at the Amazon WorkSpaces Thin Client, and you’ll notice no visible differences from the Fire TV Cube. However, instead of connecting to your entertainment system, the USB and HDMI ports connect peripherals needed for productivity, such as dual monitors, mouse, keyboard, camera, headset, and the like. Inside the device is where the similarities end. The Amazon WorkSpaces Thin Client has purpose-built firmware and software; an operating system engineered for employees who need fast, simple, and secure access to applications in the cloud; and software that allows IT to remotely manage it.
"Customers told us they needed a lower-cost device, especially in high-turnover environments, like call centers or payment processing," said Melissa Stein, director of product for End User Computing at AWS. "We looked for options and found that the hardware we used for the Amazon Fire TV Cube provided all the resources customers needed to access their cloud-based virtual desktops. So, we built an entirely new software stack for that device, and since we didn't have to design and build new hardware, we’re passing those savings along to customers.”
Learn more about Amazon WorkSpaces Thin Client, and how one of Amazon’s most familiar consumer devices has been reinvented by AWS for the enterprise.
November 27, 2023 6:00 AM
5 things you need to know about AWS re:Invent

AWS re:Invent will feature keynotes, innovation talks, builder labs, workshops, demos, service announcements, and much more.
Here are five things to expect at re:Invent 2023:
1. Generative AI everywhere. From keynotes to breakouts to hallway conversations, plan to hear a lot about generative AI.
2. AWS news and announcements. Expect service, customer, and partner announcements with the newest updates in generative AI, machine learning, and compute.
3. 5 keynotes and 17 innovation talks. AWS leaders such as AWS CEO Adam Selipsky, Swami Sivasubramanian, vice president of Data and AI at AWS, and Peter DeSantis, senior vice president of AWS Utility Computing, will share what’s top of mind for them.
4. Immersive experiences for sports fans. The re:Invent Rec Center is giving attendees a chance to watch, play, and experience games inspired by some of the major sports franchises that partner with AWS.
5. 2024 tech predictions from Amazon CTO Dr. Werner Vogels. Dr. Werner Vogels typically delivers his keynote around a key theme, covering technical ground, while also introducing some new AWS services. Concurrently, Vogels’ hotly anticipated annual tech predictions list will be published on his All Things Distributed blog.
November 26, 2023 11:00 PM
Watch: Welcome to AWS re:Invent 2023!
AWS re:Invent 2023 is a go! Here’s an early look at the excitement in Las Vegas, Nevada, so far.
Stay tuned for live updates, news, and more from AWS re:Invent, AWS’s biggest cloud event of the year.






















